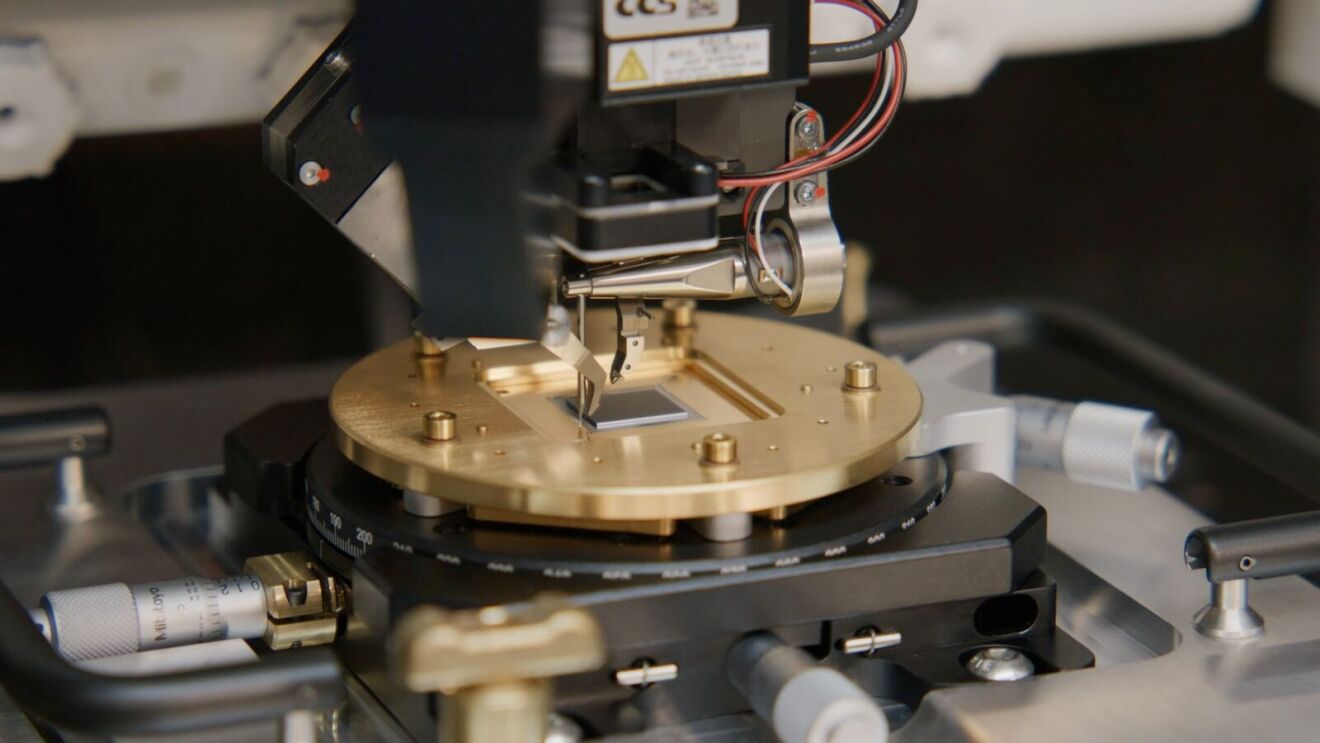
Amazon has officially entered the race for quantum supremacy announcing the launch of its first-ever quantum computing chip, Ocelot. This groundbreaking innovation places Amazon alongside tech giants like Google and Microsoft in the quest to develop powerful quantum computers that can outperform classical systems. With Ocelot, Amazon aims to solve critical challenges in quantum error correction, a major step toward making quantum computing practical.
The Power of Ocelot
One of the biggest challenges in quantum computing chips is error correction. Unlike classical computers that rely on bits, quantum computers use qubits, which are highly sensitive to interference from the external environment. Ocelot introduces a hardware-efficient approach to error correction, leveraging bosonic error correction to reduce the number of resources needed. According to Amazon, this could cut the costs of implementing error correction by up to 90% compared to traditional methods.
A Unique Architecture for Scalability
Ocelot features a hybrid design that combines two types of qubits: cat qubits and transmon qubits. Cat qubits, named after Schrödinger’s famous thought experiment, naturally suppress certain types of errors. Transmon qubits, on the other hand, act as monitors to detect and correct remaining errors. This dual approach allows Amazon to significantly reduce the number of qubits required for each logical quantum bit, making the system more scalable and efficient.
Competing with Google and Microsoft
Amazon’s quantum announcement comes shortly after Microsoft introduced its Majorana 1 chip and Google unveiled Willow. While each company is pursuing different technologies, they all share the goal of building a practical, fault-tolerant quantum computing chip. Amazon’s Ocelot prioritizes efficiency, aiming to scale up quantum computing with fewer resources and a more cost-effective approach.
Errors in quantum computing come in two main forms: bit flips and phase flips. While bit flips occur in both classical and quantum systems, phase flips are unique to quantum mechanics. Ocelot’s architecture ensures that the majority of errors are phase flips, which require less complex error correction. This significantly reduces the hardware overhead compared to existing quantum processors.
Built for Real-World Applications
Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize industries such as drug discovery, financial modeling, and materials science. However, practical quantum applications remain years away. By prioritizing hardware efficiency and error correction, Amazon hopes to accelerate the timeline for developing usable quantum systems.
The Road Ahead for Amazon
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has been working on Ocelot since 2021, investing heavily in quantum research at the AWS Center for Quantum Computing. While Ocelot is still a prototype, it represents a crucial step toward a fully functional quantum system. The next phase involves scaling up the chip, integrating more qubits, and demonstrating its ability to perform complex computations.
Despite the excitement, experts believe that commercially viable quantum computers are still 5 to 20 years away. However, Ocelot’s architecture positions Amazon as a serious contender in the race for quantum dominance.
One thing is clear Amazon’s entry into the quantum computing chip era with Ocelot marks a significant milestone.